What is CBD?
Cannabidoil (CBD) is one of more than a hundred cannabinoids found in cannabis sativa. CBD is typically the second most abundant cannabinoid after tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). All cannabinoids, including CBD, produce effects in the body by attaching to certain receptors in the body. Humans and animals alike have two receptors for cannabinoids – CB1 receptors and CB2 receptors.
The greatest number of CB1 receptors are located in the brain, while CB2 receptors are more numerous throughout the body.

CB1 Receptors
CB1 receptors activated in the brain result in an experience of pain relief, anxiety relief, mood stabilization, well-being and pleasure. Activated CB1 receptors also affect the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin and endorphins. Since CB1 receptors are most frequently located in the nervous system, they affect many of the functions in the brain and body resulting in the fine-tuning of everything to include: breathing, heart rate, tissue health and metabolic rate.
CB2 Receptors
CB2 receptors are densely located within the immune system – specifically in tissue and on white blood cells. Activated CB2 receptors are focused on stopping inflammation within the body. Active CB2 receptors alert the immune system to the presence of abnormalities within the body which ultimately leads to the body protecting itself and fighting off the abnormality.

Our oil is so much more than just CBD!
In order to understand the medicinal value of a hemp plant, you need to learn about the many compounds that are found within it. The hemp plant is made up of over 400 chemical compounds. When you use hemp oil extract, you are taking a mixture of natural compounds that work together to balance each other.
The hemp plant contains biologically active compounds called phytocannabinoids, terpenoids and flavonoids. These chemicals interact with the the brain and body chemistry to give certain effects.
What are Phytocannabinoids?
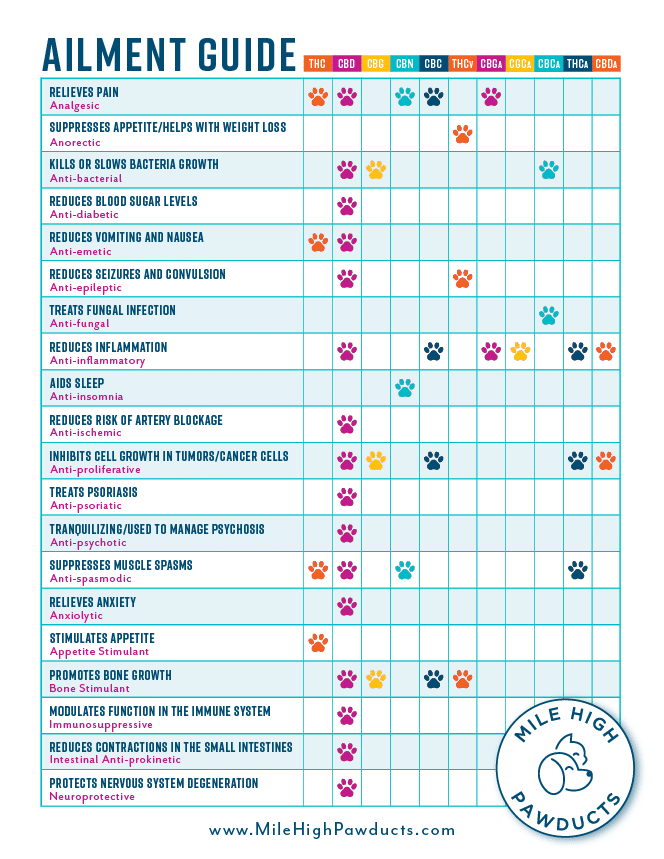
Phytocannabinoids are naturally occurring components found within the cannabis sativa. The main two phytocannabinoids are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidoil). Other phytocannabinoids found in the cannabis plant include cannabinol (CBN), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabicyclol (CBL), cannabidivarin (CBDV) and tetrahydrocannabibarin (THCB). Future research may reveal some of these to be major cannabinoids.
Each individual cannabinoid offers a variety of therapeutic benefits that are specific to its genetic structure.
What are Terpenoids?
Terpenoids (also called terpenes) are the essential oils that occur naturally and exist in all plants, trees and flowers – including the hemp plant. These oils give the hemp its odor, color and flavor. About 200 terpenoids have been discovered in the hemp plant. The terpenoid make-up of CBD oil is naturally dictated by the type of strain of which the oil was derived. Like cannabinoids, individual terpenoids offer unique therapeutic effects based on their genetics. For example, A-Pinene (which is also found in pine needles) is anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory and serves as a memory aid. Linalool (also found in lavender) helps with with anti-inflammation, anti-convulsion and anxiety. Myrcene (also found in hops) is known be a muscle relaxant and sleep aid.
Phytocannabinoids and terpenoids work together to enhance and strengthen the many therapeutic effects of our CBD oil.

What are Flavonoids?
Flavonoids are compounds that give plants their pigmentation, filter ultraviolet rays, attract pollinators and prevent plant disease. About 20 flavonoid compounds have been found in the hemp plant. Flavonoids have been shown in laboratory studies to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. They also have anti-fungal, anti-bacterial, anti-viral, anti-cancer and anti-allergic activity.
Each individual cannabinoid offers a variety of therapeutic benefits that are specific to its genetic structure.
What is the Entourage Effect?
Not all of the phytocannabinoids have been thoroughly studied, but those that have are found to have their own medicinal effects when isolated from the other cannabinoids. When used together as they occur naturally in the whole plant, they balance each other in a synergistic action first called “the entourage effect” by Raphael Mechoulam, PhD. Dr Mechoulam was the first to isolate THC and CBD in the early 1960s.
The “entourage effect” means that the cannabinoids work better together than when isolated from one another.
Example of synergistic enhancement: both THC and CBD, when given separately, have been found to have pain-relieving properties, but studies have shown that CBD enhances pain relief when used together with THC compared to THC used by itself.
Example of opposing effects: CBD can decrease psycho-activity, memory loss and increased heart rate which are all effects caused by THC.
Each individual cannabinoid offers a variety of therapeutic benefits that are specific to its genetic structure.